Sometimes we need to take screenshot of our desktop or webpage , though print screen provide the facility but we can also do with python. I am using python screen shot options to take some screen shot of my web page I created with flask( a light weight website development platform which uses python.). First of all you need to have a module named pyscreenshot.
You can install
pyscreenshot from the pip utility , provided you have installed pip previously. If you don't know about pip, see here -
After you have installed the pip utility, you can easily install pyscreenshot by using the below command -
c:\> pip install pyscreenshot
It will download and install pyscreenshot module. Now let's see how to take a screenshot -
** First of all create a new file and named it anything you want. I named it imagegrab.py. And write the below line to it.
import pyscreenshot
def imagegrab():
image=pyscreenshot.grab(bbox=(10,10,510,510)).show()
** Save the file. Now you can run the program through idle but it won't show anything.
** To run the program properly - open the command prompt from the same directory by holding shift and right click or open command prompt and navigate to the directory of the program.
** Type the following to the command prompt -
C:\programs> python -m imagegrab
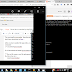
It will show the output like below -
The screen shot is cropped by bbox funtion with bbox(x1,y1,x2,y2) where (x1,y1) is the location of the top left corner or a starting point and (x2,y2) is the end point. You can also grab the screen shot directly to file by using the pyscreenshot.grab_to_file(filename) function. Write help(pyscreenshot) for more on this topic.
But I am disappointed with this pyscreenshot as I was having difficulties with integrating this simple program to flask. Luckilty matplotlib helped to get the screenshot.